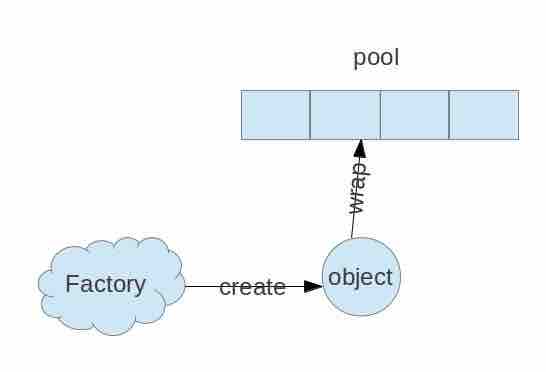
common-pool2 核心组件
-
ObjectPool:实现对对象的存取和状态管理的池实现;如:线程池,数据库连接池等。 PooledObject:池化对象,将对象包装成 PooledObject 后放入池中。添加了一些附加信息,比如说状态信息,创建时间,激活时间等。 PooledObjectFactory:工厂类,负责具体对象的创建、初始化,对象状态的销毁和验证等。
关于 3 大组件的具体方法等信息,参考 Apache Commons-pool2。
配置参数
-
lifo:连接池放池化对象的方式,默认为 true。
true:放在空闲队列最前面
false:放在空闲队列最后面
-
fairness:等待线程拿空闲连接的方式,默认为false(非公平锁)。
-
maxWaitMillis:当连接池资源耗尽时,调用者最大阻塞的时间,超时将抛出异常。单位:毫秒数;默认为 -1,表示永不超时。
-
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis:连接空闲的最小时间,达到此值后空闲连接将可能会被移除。负值(-1)表示不移除;默认值1000L * 60L * 30L。
-
softMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis:连接空闲的最小时间,达到此值后空闲链接将会被移除,且保留 minIdle 个空闲连接数。
-
numTestsPerEvictionRun:把空闲对象移出池中,每次操作的个数,默认值 3。
-
testOnBorrow:向调用者输出“链接”资源时,是否检测是有有效,如果无效则从连接池中移除,并尝试继续获取。默认为 false。设置为 true 对性能影响较大,建议保持默认值。
-
testWhileIdle:向调用者输出“链接”对象时,是否检测它的空闲超时;默认为 false。如果“链接”空闲超时,将会被移除;建议保持默认值。默认值 false。
-
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis:“空闲链接”检测线程,检测的周期。如果为负值,表示不运行“检测线程”。默认值 -1L。
-
maxTotal:链接池中最大连接数,默认值 8。
-
maxIdle:连接池中最大空闲的连接数,默认为 8。
-
minIdle:连接池中最少空闲的连接数,默认为 0。
配置示例
/**
* 推荐设置 maxTotal == maxIdle,
* 如果 maxIdle < maxTotal,比如 maxTotal = 500, maxIdle = 200,
* 在持续高并发的情况下,很容易出现 idleObjectNum > maxIdle 的情况,导致多余的空闲连接被舍弃,socket 为 time_wait 状态;
* 之后由于新的大量并发请求,又需要创建新的 socket 连接来处理,循环这个过程最终会导致产生大量 time_wait 连接,本地端口被占用完。
*/
poolConfig.setMaxTotal(500); // 设置稍微大一些已应付突发请求
poolConfig.setMaxIdle(500);
poolConfig.setMinIdle(10);
poolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(3000);
/**
* 每 15s 对池中对象进行一次检查,如果空闲时间超过 5s,则把空闲对象移出池中,每次最多移出 10 个对象;
* 如果池中空闲对象 <= 10(minIdle),则不进行移除操作。
*/
poolConfig.setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(15000);
poolConfig.setSoftMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(5000);
poolConfig.setNumTestsPerEvictionRun(10);
源码分析
从池中获取对象
// 空闲对象集合,是一个双向队列
private final LinkedBlockingDeque<PooledObject<T>> idleObjects;
public T borrowObject(final long borrowMaxWaitMillis) throws Exception {
assertOpen();
/**
* AbandonedConfig:这个类的作用主要是用来清理无用对象,避免内存泄漏,默认为 null。
* 参考:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000006889810
*/
final AbandonedConfig ac = this.abandonedConfig;
if (ac != null && ac.getRemoveAbandonedOnBorrow() &&
(getNumIdle() < 2) &&
(getNumActive() > getMaxTotal() - 3) ) {
removeAbandoned(ac);
}
PooledObject<T> p = null;
// Get local copy of current config so it is consistent for entire
// method execution
final boolean blockWhenExhausted = getBlockWhenExhausted();
boolean create;
final long waitTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (p == null) {
create = false;
// 1. 从对象池中获取一个对象
p = idleObjects.pollFirst();
if (p == null) {
// 2. 如果没有获取到,那么新建一个对象;注:不一定会成功,比如已创建对象达到 maxTotal
p = create();
if (p != null) {
create = true;
}
}
// 3. blockWhenExhausted 默认为 true:即如果没有获取到对象,那么等待 maxWaitMillis,如果在这段时间内还是没有获取到对象;或者 blockWhenExhausted 设置为 false,则直接抛出异常。
if (blockWhenExhausted) {
if (p == null) {
if (borrowMaxWaitMillis < 0) {
p = idleObjects.takeFirst();
} else {
p = idleObjects.pollFirst(borrowMaxWaitMillis,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
if (p == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException(
"Timeout waiting for idle object");
}
} else {
if (p == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Pool exhausted");
}
}
// 4. 状态重置。此时,p 肯定不等于 null。但是,有可能 p 已经被空闲链接检测线程标记为废弃。因此需要做一步判断:如果 p 的状态为空闲(IDLE),则标记为已分配(ALLOCATED);如果 p 的状态为(EVICTION),则标记为 EVICTION_RETURN_TO_HEAD,并且重置 p = null,即刚才获取的对象不可用。
if (!p.allocate()) {
p = null;
}
// 5. 如果 p == null,那么从步骤 1 开始,重新尝试获取
if (p != null) {
try {
// 6. 如果 p != null,调用 factory.activateObject(p) 方法:该方法的主要作用是当对象从池中移出时,可以对该对象做一些额外操作。
factory.activateObject(p);
} catch (final Exception e) {
try {
destroy(p);
} catch (final Exception e1) {
// Ignore - activation failure is more important
}
p = null;
if (create) {
final NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException(
"Unable to activate object");
nsee.initCause(e);
throw nsee;
}
}
// 7. 如果满足以下条件(比如设置了 testOnBorrow 为 true),那么需要对该对象进行测试是否正常;如果不正常,销毁该对象
if (p != null && (getTestOnBorrow() || create && getTestOnCreate())) {
boolean validate = false;
Throwable validationThrowable = null;
try {
validate = factory.validateObject(p);
} catch (final Throwable t) {
PoolUtils.checkRethrow(t);
validationThrowable = t;
}
if (!validate) {
try {
destroy(p);
destroyedByBorrowValidationCount.incrementAndGet();
} catch (final Exception e) {
// Ignore - validation failure is more important
}
p = null;
if (create) {
final NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException(
"Unable to validate object");
nsee.initCause(validationThrowable);
throw nsee;
}
}
}
}
}
updateStatsBorrow(p, System.currentTimeMillis() - waitTime);
return p.getObject();
}
清理空闲时间超过 softMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis 的对象
// 空闲对象集合,是一个双向队列
private final LinkedBlockingDeque<PooledObject<T>> idleObjects;
public void evict() throws Exception {
assertOpen();
if (idleObjects.size() > 0) {
PooledObject<T> underTest = null;
final EvictionPolicy<T> evictionPolicy = getEvictionPolicy();
synchronized (evictionLock) {
final EvictionConfig evictionConfig = new EvictionConfig(
getMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(),
getSoftMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(),
getMinIdle());
final boolean testWhileIdle = getTestWhileIdle();
// 一次最多清理 numTests 个对象
for (int i = 0, m = getNumTests(); i < m; i++) {
if (evictionIterator == null || !evictionIterator.hasNext()) {
// 空闲对象集合的游标:如果 lifo 为 true,从队尾向队首扫描;如果 lifo 为 false,从队首向队尾扫描
evictionIterator = new EvictionIterator(idleObjects);
}
if (!evictionIterator.hasNext()) {
// Pool exhausted, nothing to do here
return;
}
try {
underTest = evictionIterator.next();
} catch (final NoSuchElementException nsee) {
// Object was borrowed in another thread
// Don't count this as an eviction test so reduce i;
i--;
evictionIterator = null;
continue;
}
// 状态重置。如果对象状态为 IDLE,那么重置为 EVICTION;如果对象状态为其他,则不清理
if (!underTest.startEvictionTest()) {
// Object was borrowed in another thread
// Don't count this as an eviction test so reduce i;
i--;
continue;
}
// User provided eviction policy could throw all sorts of
// crazy exceptions. Protect against such an exception
// killing the eviction thread.
boolean evict;
try {
// 判断对象是否符合清理条件
evict = evictionPolicy.evict(evictionConfig, underTest,
idleObjects.size());
} catch (final Throwable t) {
// Slightly convoluted as SwallowedExceptionListener
// uses Exception rather than Throwable
PoolUtils.checkRethrow(t);
swallowException(new Exception(t));
// Don't evict on error conditions
evict = false;
}
// 如果符合条件,则销毁对象
if (evict) {
destroy(underTest);
destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet();
} else {
if (testWhileIdle) {
boolean active = false;
try {
factory.activateObject(underTest);
active = true;
} catch (final Exception e) {
destroy(underTest);
destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet();
}
if (active) {
if (!factory.validateObject(underTest)) {
destroy(underTest);
destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet();
} else {
try {
factory.passivateObject(underTest);
} catch (final Exception e) {
destroy(underTest);
destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
}
if (!underTest.endEvictionTest(idleObjects)) {
// TODO - May need to add code here once additional
// states are used
}
}
}
}
}
final AbandonedConfig ac = this.abandonedConfig;
if (ac != null && ac.getRemoveAbandonedOnMaintenance()) {
removeAbandoned(ac);
}
}